This post summarizes research from the January 2013 edition of Wood Bioenergy US (WBUS).
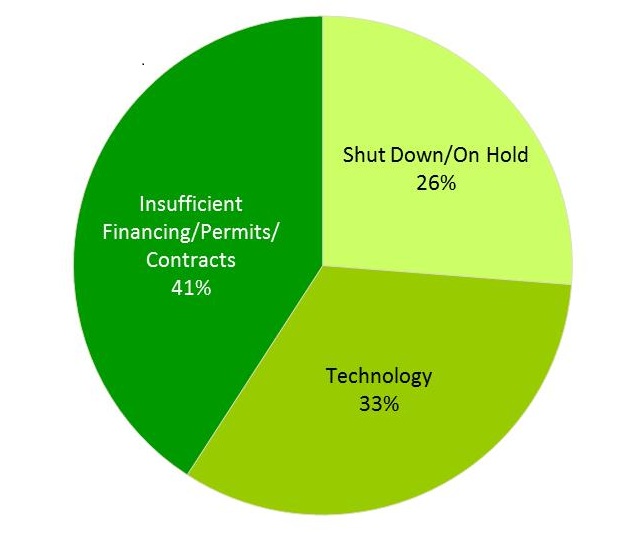
Viable wood bioenergy projects can secure competitive financing. In U.S. capital markets, primary sources of financing for these projects include private equity, project finance, grants, loans and bond issuances. Decreased availability of financing represents one of the top three responses – along with legislative uncertainty and low natural gas prices – from managers of idled or failed wood bioenergy projects tracked by Forisk from 2009 through 2012. Bioenergy plants must compete with other bioenergy projects for financing, as well as with projects of all types in different industries. Of the 164 projects that fail Forisk’s viability screening, at least 41% explicitly lack sufficient access to capital to advance towards construction.
Figure:
Reasons Announced Wood Bioenergy Projects Fail Viability Screening
Recent announcements regarding financing for projects indicate how investors view different bioenergy technologies and markets. Financing cannot be ordered at the drive-thru window. The ability to secure financing from a lender indicates some level of confidence and manageable risk in the eyes of investors. It requires project developers to demonstrate a robust business model or ongoing concern with a proven track record. For wood bioenergy projects with unproven technologies, developers must turn to government funding sources or to private equity investors with appetites for higher risk. The wood pellet industry, while facing uncertain growth, has established its viability; a track record of operational success is the best proof of creditworthiness, affirmed by the sector’s access to cheaper, traditional debt financing. Cellulosic ethanol and other biofuel projects remain high risk with a challenging road to commercialization. These projects rely on government funding, such as programs through the Department of Defense, and costly private equity.
WBUS Market Update: As of January 2013, WBUS counts 461 announced and operating wood bioenergy projects in the U.S. with total, potential wood use of 132.9 million tons per year by 2023. Based on Forisk analysis, 296 projects representing potential wood use of 76.2 million tons per year pass basic viability screening. To download the free WBUS summary, click here.

Leave a Reply