This post is an excerpt from the Q4 2025 Forisk Research Quarterly (FRQ), which includes forest industry analysis and timber price forecasts for North America.
Introduction
Pulp and paper mill closures over the last three years surprised many in the forest industry. As large consumers of low-value fiber, pulp mills aid sound forest management and provide markets for residual products generated by mills. Each pulp mill closure, or shift away from virgin wood to recycled fiber, affects local wood baskets. When mills close or change, we ask questions to better understand implications for timberland investors, lumber manufacturers, and wood fiber consumers. What factors contributed to the declining demand for wood pulp? Why were these mills selected for closure? In the Q4 2025 Forisk Research Quarterly, we explore these questions and where the industry may go from here.
Pulp Mill Risk Analysis
Forisk analyzed 29 pulp mills that closed in the U.S. since 2019 and identified four factors that contributed to mill closures: 1) exposure to weak end markets, 2) lack of investment (particularly in pulping infrastructure), 3) age of the pulp mill recovery boiler, and 4) challenging procurement logistics. Forisk developed a framework to screen open pulp mills for risk of future closures from these factors and applied that framework to mills in the U.S. Pacific Northwest, U.S. South, and U.S. North in the Forisk Research Quarterly report.
Forisk tracks one of these factors, lack of investment, as part of our mill database research program. The pulp and paper sector is the most capital-intensive sector of the forest products industry. Firm initiatives and consolidations affect capital allocation decisions. Closing non-performing assets and high-cost mills are efforts to improve the use of shareholder resources. As such, lack of capital investment can indicate at-risk mills, while investments signal a commitment to operating a facility.
While 11 mills that closed since 2019 had capital investments, as indicated in Figure 1 from Forisk, only three invested in pulping components. Investments in pulping infrastructure, including the recovery boiler, digester, and woodyard, may indicate a higher commitment to the facility than non-pulping investments.
The full risk analysis of open pulp mills, including regional mill maps, is published in the Q4 2025 Forisk Research Quarterly.
To learn more about the Forisk Research Quarterly (FRQ), click here or email Nick DiLuzio at ndiluzio@forisk.com.
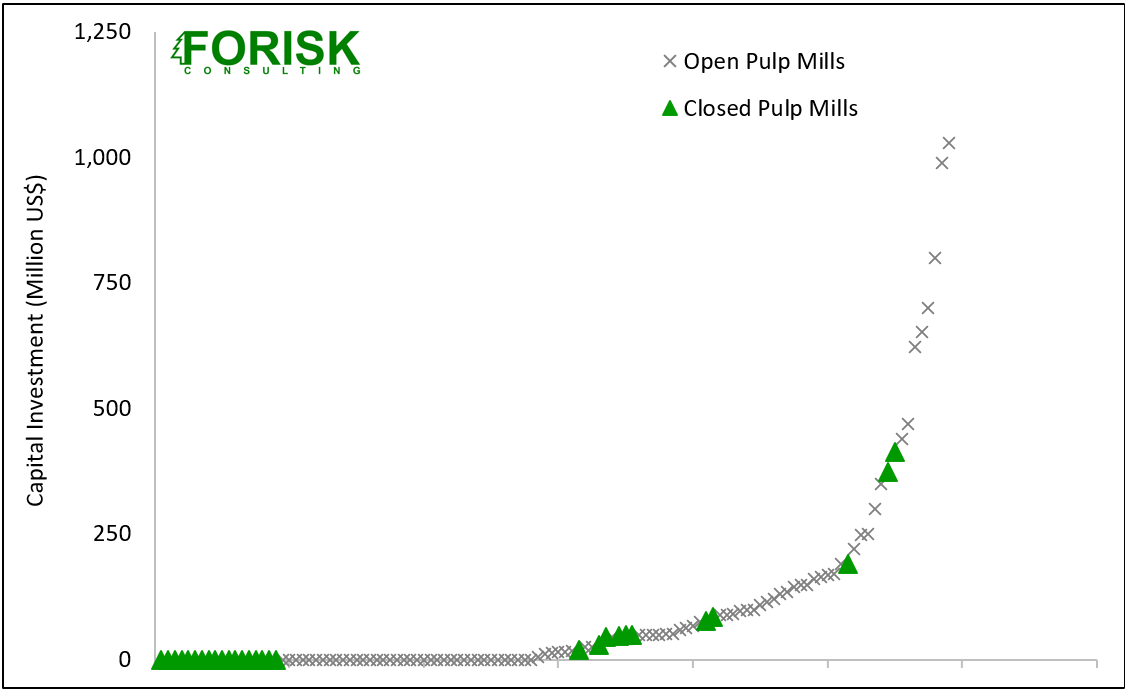
Data source: Forisk Consulting
Note: Includes mills that have closed since 2019
Includes 12 announced investments scheduled for completion in 2025 – 2028.

Leave a Reply